Music-driven group choreography는 다양한 어려움이 있지만, 산업 분야에 응용할 분야가 상당히 많기 때문에 최근 들어 연구가 활발하게 진행되고 있는 분야라고 한다.
하지만, 대부분의 최근 연구들은 high-fidelity long-term motion을 만들지 못하거나 controllable한 경험을 허용하지 않는다. 그래서 이 논문에서는 high-quality, customizable한 group dance generation을 consistency와 diversity를 효율적으로 제어함으로써 해결하고자 했다고 한다.
구체적으로 diffusion-based 방식을 사용해서 input music에 coherent하면서 flexible한 dancer 수와 long-term group dance를 조절할 수 있게 하였다고 한다.
궁극적으로 Group Contrastive Diffusion [GCD] 전략을 제안해서 dancer와 group 간의 connection을 강화하고 classifier-guidance sampling 기법으로 생성된 group animation에서의 consistency와 diversity level을 컨트롤 할 수 있게 하였다고 한다.
Introduction

기존의 문제점
- The task of producing cohesive and expressive choreography for a group of dancers has received limited attention
- Complex relationship between music and human motion, the diverse range of motions required for group performances, and the insufficient dataset → Music-Driven Group Choreography에서 AIOZ-GDance dataset을 만듦
- Different from solo dance, group dance involves coordination and interaction between dancers, making it crucial and challenging to establish correlations between motion series within a group
Music-Driven Group Choreography
Music-driven choreography is a challenging problem with a wide variety of industrial applications. Recently, many methods have been proposed to synthesize dance motions from music for a single dancer. However, generating dance motion for a group remains an
arxiv.org
Dancer들의 움직임에서 consistency와 diversity를 탐색하는 것은 자연스럽고 표현력 좋은 안무를 생성하기 위해 굉장히 중요하다고 한다. 그래서 이 논문에서는 group dance generation에서 consistency와 diversity를 control할 수 있는 기법을 개발하는 것을 목표로 삼았고, encoder가 group dance movement 사이에서 key target들을 포착하는 Group Contrastive Diffusion 전략을 제안하게 되었다고 한다.
이를 위해 DDPM [Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model]을 핵심 모델로 사용해서 group dance generation에서의 diversity와 consistency 간의 trade-off를 효과적으로 제어할 수 있었고, guided sampling process가 이 과정에서 큰 역할을 했다고 한다. 또한 dancer들과 group 사이의 association을 학습하는 encoder를 결합해서 특정한 dance style, music genre, long-term chorus에 consistent한 상태를 유지할 수 있도록 하였다.
Contribution
- We introduce contrastive diffusion, the first denoising diffusion approach for music-driven group choreography. Our model is able to generate high-fidelity and diverse group dancing motions that are aligned with the input music.
- We develop a method to trade-off between the consistency and diversity of generated group motions. Our framework allows users to control and generate different outputs from a single piece of input music
- Extensive experiments along with user study evaluations demonstrate SOTA performance of our model in synthesizing group choreography animation, as well as creating long dance motion sequences while maintaining the coherency among dancers
Methodology
Background

이 논문에서 dance는 24-joint SMPL model로 pose의 sequence 형태로 구성했다고 한다. 그리고 모든 joint에 6DoF [6 Degree of Freedom]를 적용했다고 한다.
이로 인해 rotation vector의 uniqueness와 continuity를 보장해서 딥러닝을 학습하는데 더 도움이 된다고 한다.
Thanks to the sampling process of the diffusion model, we can effectively control the consistency and diversity in the generated sequence
Forward Process of Diffusion Model

Reverse Process of Diffusion Model

Group Diffusion Denoising Network
Transformer-based architecture를 이용해서 한방에 전체 sequence를 생성하였다. Output이 나오게 되면 다시 input으로 들어가서 다음 frame을 예측하는 Auto-regressive 방식을 적용해서 임의의 long motion dance sequence를 freezing 없이 생성할 수 있었다고 한다.


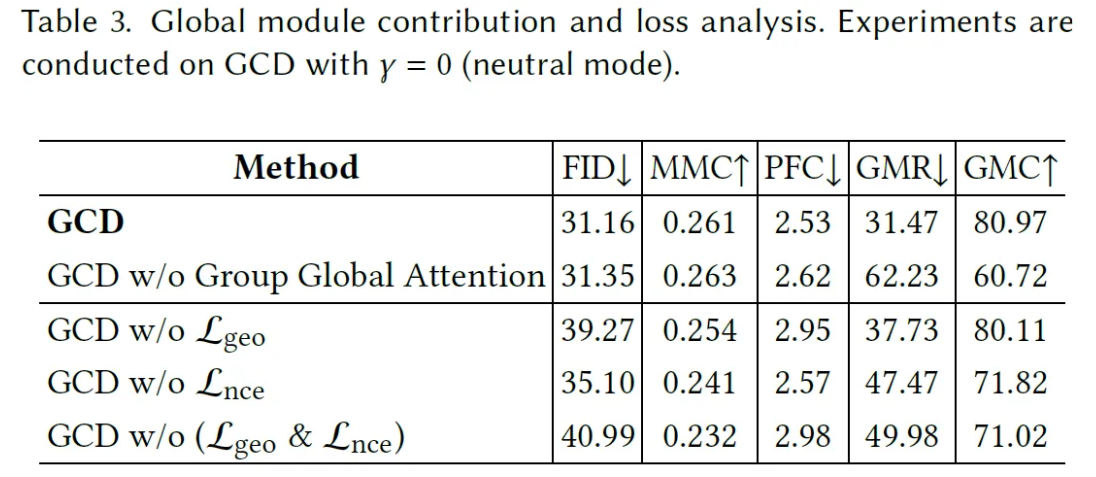
Group Global Attention
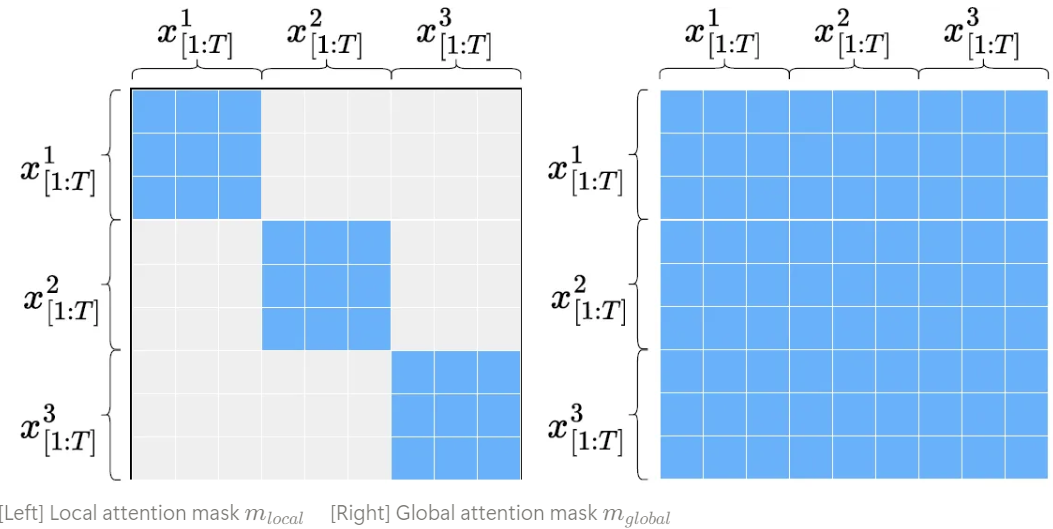
Group 내의 모든 dancer들의 움직임에서 coherency와 non-collision을 보장하기 위해 masked attention mechanism을 통해 global attention을 수행했다고 한다.
이를 통해 global receptive field에서 다른 모든 dancer들과 완전히 attend할 수 있게 되었다. 그 후에 Group Modulation을 적용해서 group embedding information 안에서 group constraint를 강화하였다고 한다.
Latent style vector를 통해 synthesized image를 다루는 StyleGAN에 영감을 받아서 input music으로 부터 group embedding information을 학습하는 것을 목표로 정해서 group dance generation process를 control 하고자 하였다고 한다.

Group Modulation
To better apply the group information constraints to the learned hidden features of the dancers, we adopt a Group Modulation layer that learns to adaptively influence the output of the transformer attention block by applying an affine transformation to the intermediate features based on the group embedding w
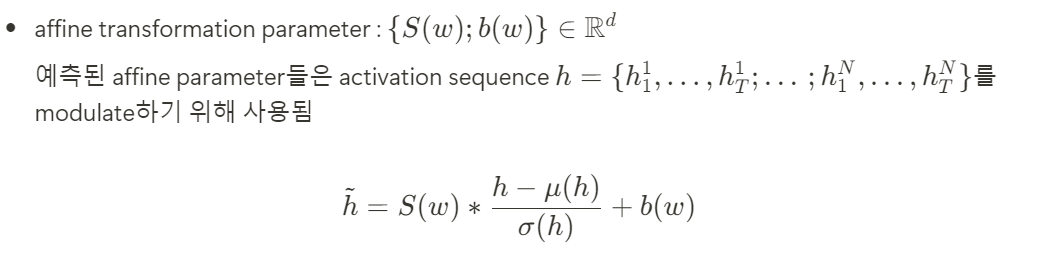
이 연산을 통해 각각의 motion의 activated hidden motion feature들이 통합된 group representation으로 shift되고 마지막에 output feature들이 linear layer에 의해 원래의 motion dimension으로 투영되게 되어 최종 예측 결과를 얻게 됨
Contrastive Diffusion for Controllable Group Dance
Contrastive Diffusion

생성된 group dance [data]와 group embedding [context] 간의 association을 향상시키기 위해 이들의 mutual information을 Contrastive Encoder로 극대화 하는 것을 목표로 정했다고 한다.
Encoder는 생성된 group dance sequence와 group embedding을 input으로 받아서 이 둘 간의 correspondence를 나타내는 score를 output으로 내보낸다.
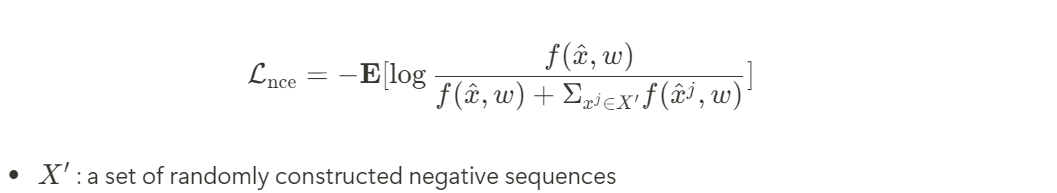
Contrastive objective를 이용해서 Contrastive Encoder가 consistency와 diversity를 구분하기를 기대했다고 한다.

This is because mixing a sample with dancers from different groups is likely to result in substantially distinctive movements between each dancer, making it a group dance sample with high degree of diversity.
주목할 점은, negative sample들 역시 music과 맞아야 한다는 점이다. 특히 negative sample들은 denoising network로 부터 얻은 결과물이기 때문에 network는 positive sample만 생성하도록 되어 있다는 점에서 music과 sync를 잘 맞춰야 한다.
Diversity vs Consistency
Contrastive Encoder $f(x_m,w)$를 사용해서 classifier guidance를 확장시켜서 generation process를 통제하고자 했다고 한다. 이를 위해 reverse diffusion process의 평균을 Contrastive Encoder의 log gradient descent를 따라서 옮겼다고 한다.
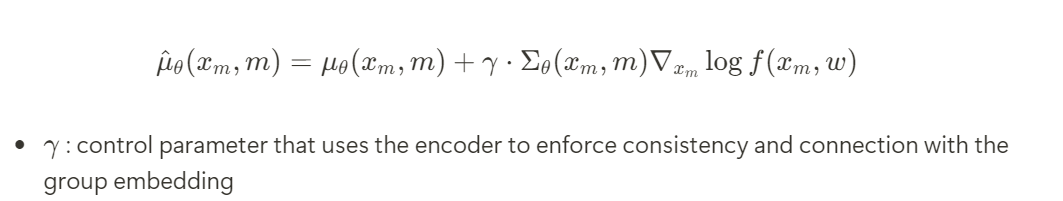
Contrastive Encoder는 high-consistency와 high-diversity를 구분하기 위해 학습되었기 때문에 이것의 gradient는 trade-off process를 제어하기에 아주 좋은 guidance signal을 제공하게 된다고 한다.
Experiments
Implementation Detail
- The hidden layer of all the MLPs consists of 512 units followed by GELU activation
- Attention adopts a multi-head scheme with 8 attention heads
- Feature-wise linear modulation [FiLM] after each attention layer to strengthen the influence of the conditioning context
- Append 2-layer feed forward network with a feed forward size of 1024 to enhance the expressivity of the learned features after each attention layer
- Extract features from the raw audio signal by leveraging the representations from the frozen Jukebox
- Group Diffusion Denoising Network is comprised of $L=5$ stacked Music-Motion Transformer and Group Global Attention blocks, along with 2 transformer encoder layers
Training

Experimental Settings
Dataset
AIOZ-GDance Dataset을 사용해서 7개의 dance style과 16개의 music genre를 커버했다고 한다.
Metric
Metric의 경우 Frechet Inception Distance [FID], Motion-Music Consistency [MMC], Generation Diversity [GenDiv], Physical Foot Contact Score [PFC], Group Motion Realism [GMR], Group Motion Correlation [GMC], Trajectory Intersection Frequency [TIF]를 사용했다고 한다.
Baselines
FACT, Transflower, EDGE, GDanceR과 비교했다고 한다.
Results
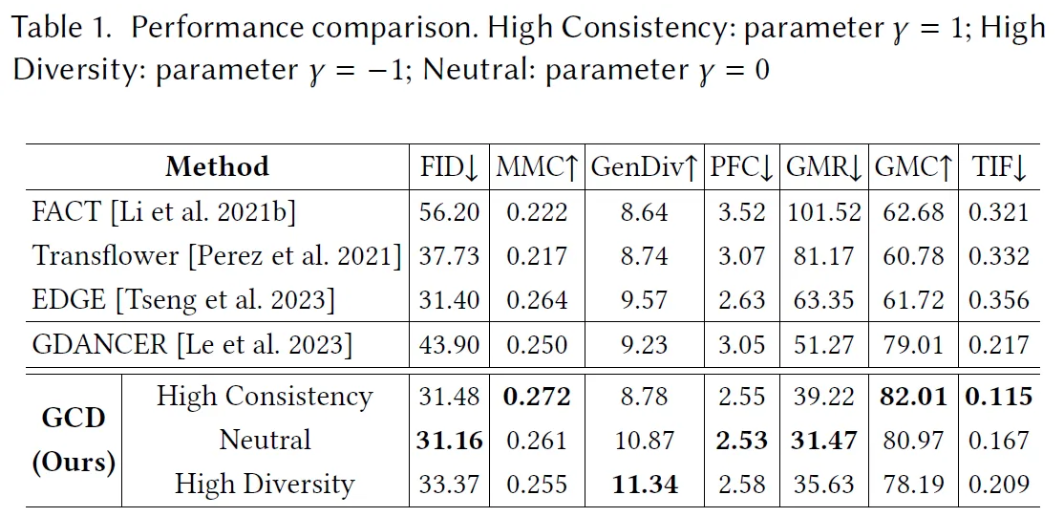


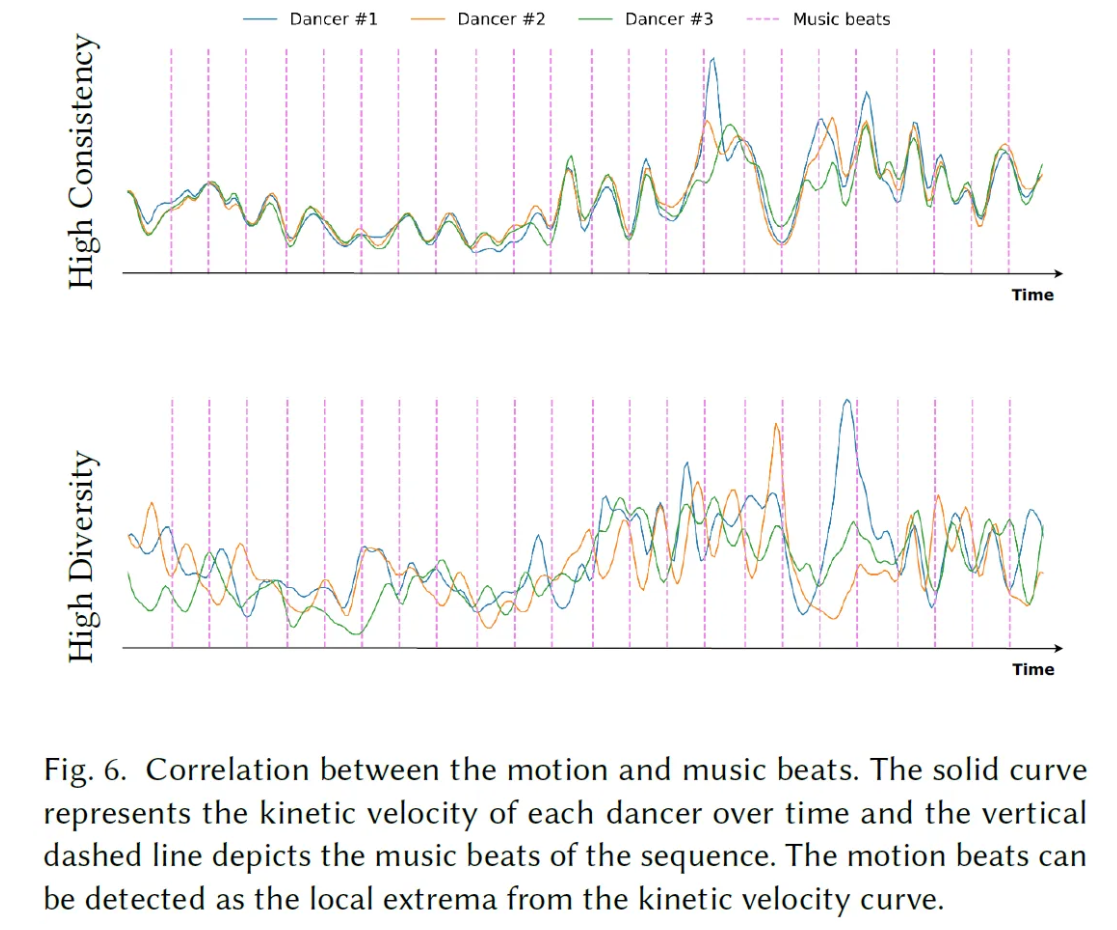

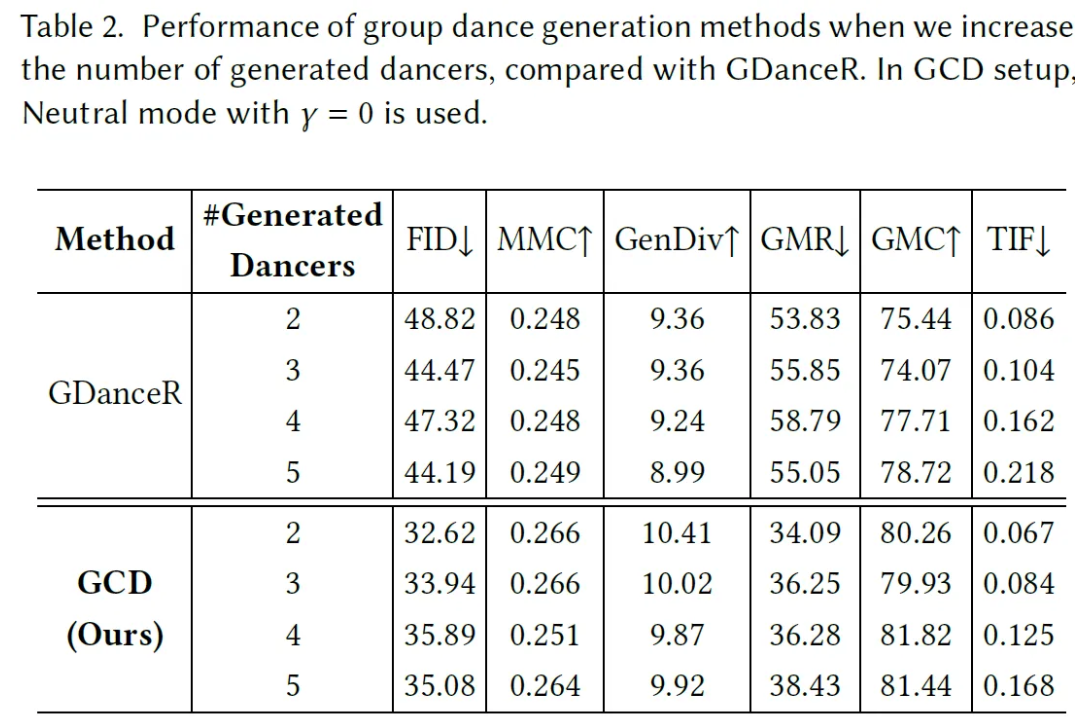
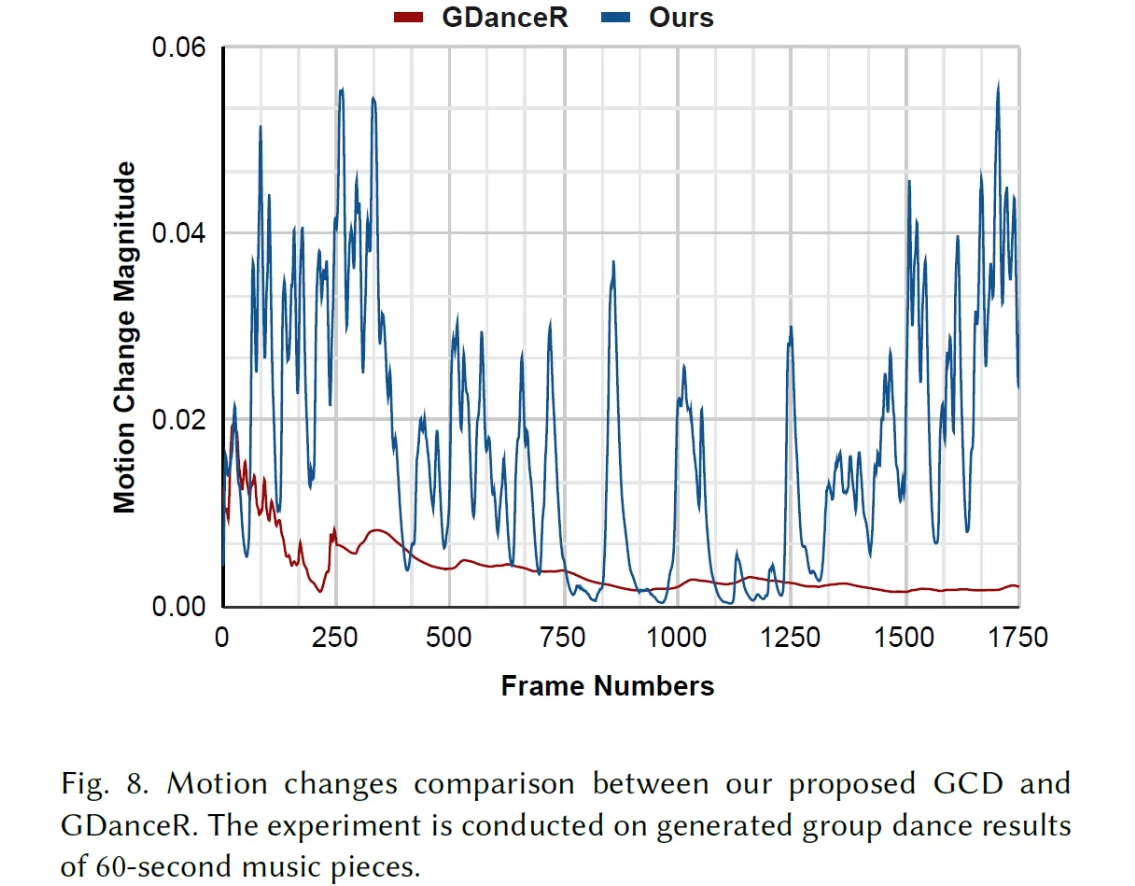

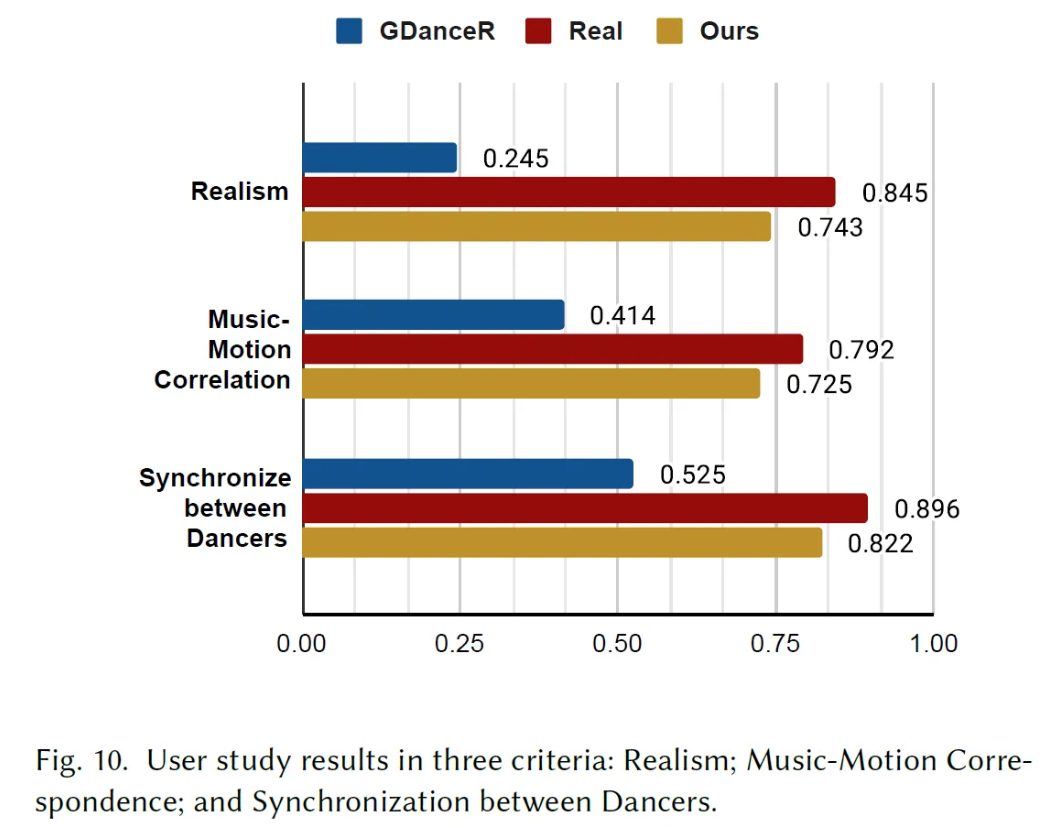
User Study
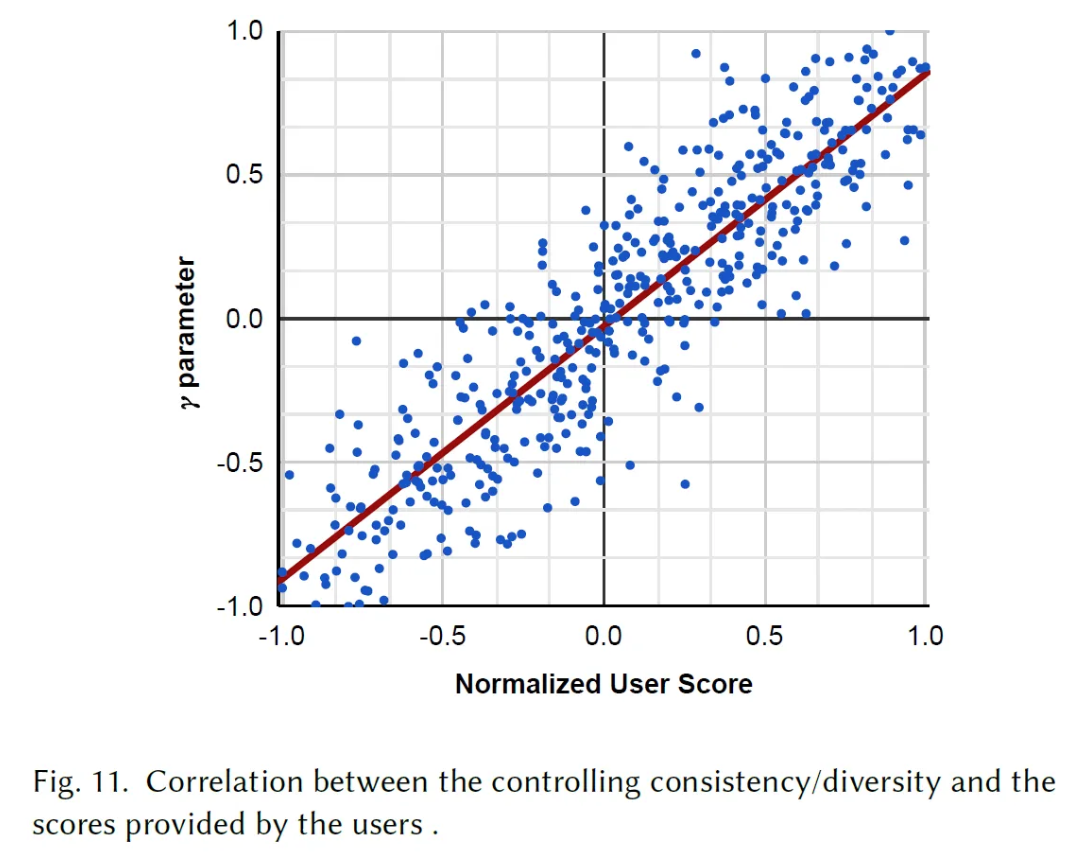
Discussion and Conclusion
Although our model can synthesize semantically faithful group dance animation with effective coordination among dancers, it does not capture clear physical contact between dancers such as hand touching. This is because the data we used in training does not contain such detailed hand motion information. Additionally, while our method offers a trade-off between diversity and consistency, achieving perfecet alignment between high-diversity movements and music remains a challenging task
We have introduced GCD, a new method for audio-driven group dance generation that effectively controls the consistency and diversity of generated choreographies