
논문 출처
https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377
Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners
This paper shows that masked autoencoders are scalable self-supervised learners for computer vision. Our MAE approach is simple: we mask random patches of the input image and reconstruct the missing pixels. It is based on two core designs. First, we
arxiv.org
Abstract
이 논문에서는 MAE [Masked Autoencoder]가 computer vision 분야에서 scalable self-supervised learners라는 것을 보여준다. 이를 위해 input image의 random patch를 마스킹하고 missing patch에 대해 reconstruct를 하는 방식으로 이를 보여주고 있다.
- Asymmetric encoder-decoder architecture + lightweight decoder
- 75% 같이 높은 비율로 masking을 하는 것이 유의미한 self-supervised 결과를 도출
이 두 가지 design을 결합한 것은 크기가 큰 model을 효과적으로 training 시킬 수 있다.
Introduction
GPT와 BERT 같은 NLP 분야에서의 MAE는 개념적으로는 간단하다. Data의 일부를 제거한 뒤 제거한 내용을 예측하기 위해 학습한다. MAE의 idea는 NLP 뿐만 아니라 Computer Vision 분야에도 적용이 가능하다. 그러나 vision 분야에서의 autoencoding 기법의 발전은 더디었고 다음과 같은 질문을 불러왔다.
“What makes masked autoencoding different between vision and language?"

- 최근까지도 vision 분야는 CNN [Convolutional Neural Network]가 지배적이였기 때문에 mask token이나 positional embedding을 활용하기 힘들었었는데 ViT [Vision Transformer]의 등장으로 구조적인 차이가 줄어들었다.
- 그러나 NLP와 Vision의 Information density는 Language의 경우 인간이 만들어낸 signal의 의미이기 때문에 매우 semantic하고 information-dense하므로 단어 하나하나에 의미가 있고 . 그러나 Image의 경우 이웃하는 patch들로부터 missing patch가 cover될 수 있다.
- Text와 image를 reconstructing할 때 decoder는 각각 다른 역할을 한다. Vision에서는 decoder는 semantic level이 낮은 pixel을 reconstruct하는 역할을 하고 NLP에서의 decoder는 풍부한 semantic 정보를 갖고 있는 missing word를 예측하는 역할을 한다.
Related Work
Masked Language Modeling
BERT와 GPT 같은 masked language modeling과 autoregressive counterpart는 NLP에서 매우 성공적인 pre-training 기법이다. 이 기법들은 input sequence로 missing content를 예측하기 위한 model의 training을 실행한다.
Autoencoding
Autoencoding은 특징을 훈련하기 위한 classic한 기법이다. Autoencoder의 경우 classic한 DAE [Denoising Autoencoder]의 경우 masking한 pixel들이나 color channel들을 없앤 것과 같이 input signal을 corrupt한 뒤 원래의 uncorrupt한 image를 다시 만들기 위해 훈련시키는 autoencoder의 class이다.
Masked Image Encoding
Masking으로 인해 변질된 image로 부터 특징을 배우는데 쓰인다. NLP에서의 성공에 영향을 받아 최근의 연구들은 Transformer를 기반으로 하고 ViT도 self-supervised learning을 위해 masked patch prediction을 연구한다. 또한 더 최근에 발표된 BEiT의 경우 Transformer를 self-supervised learning에 적용했다.

Approach
MAE는 기본적으로 Autoencoder의 concept를 따라간다. Input signal을 latent representation시키고 다시 원래의 signal로 reconstruct하는 과정을 반복한다. 다만 기존의 Autoencoder와 다른 점은 Asymmetric design으로 구성한 점인데 encoder에는 masking 되지 않은 token만 사용하고 decoder에는 encoder보다 조금 더 가볍게 modeling함과 동시에 mask token을 붙여서 reconstruct 시킨다.
Masking
ViT에 따라 image를 regular non-overlapping patch들로 나눈 뒤 patch들의 일부를 sampling하여 나머지를 masking한다.
“Our sampling strategy is straightforward: we sample random patches without replacement, following a uniform distribution"
흔히 이를 [random sampling] 이라고 부른다.
높은 비율의 masking으로 random sampling을 하는 것은 일반적으로 redundancy를 없애기 때문에 이웃하는 patch들로 유추를 하는 것은 쉽게 해결되지 않는다. Uniform한 분포는 잠재적인 center bias를 막고 매우 sparse한 input은 매우 효과적인 encoder를 design할 기회를 만들어준다.
MAE encoder
MAE의 encoder는 ViT이지만, masking하지 않은 patch에만 적용되어 있다. 일반적은 ViT 처럼 MAE의 encoder는 추가적인 positional embedding들과 함께 linear projection을 함으로써 patch를 embedding한다. 그런 뒤 output을 transformer block들로 연산하는 과정을 진행한다.
그러나 MAE의 encoder는 25% 같이 매우 작은 encoder에만 적용이 된다.
Msked patch들은 제거되었고 더이상 mask된 token은 사용되지 않는다. 이는 매우 큰 encoder를 매우 적은 연산과 메모리로 실행할 수 있게 한다. 그리고 full set의 경우는 lightweight decoder로만 handling된다.
MAE decoder
MAE decoder에 주어지는 input은 encoding된 patch들과 mask된 token들을 포함한 full set token들이다.
MAE decoder는 image reconstruction task를 수행하기 위해 pretraining을 하는 동안에만 사용된다. 따라서 decoder architecture는 encoder와 독립적인 방식으로 flexible하게 design되어 있다.
Reconstruction target
MAE는 input을 각각의 masked patch에 대해 pixel값을 예측함으로써 reconstruct한다. Decoder의 output에서의 각각의 element는 patch를 나타내는 pixel 값들의 vector이고 decoder의 마지막 layer는 patch에서 output channel의 개수와 pixel value들의 개수가 같은 linear projection이다. Decoder의 output은 reconstructed image를 만들기 위해 reshape되고, loss function은 pixel 공간에서 원래의 image와 reconstructed된 image 간의 MSE loss로 구해진다. 이 loss 값을 BERT와 유사하데 masked patch들로만 구한다.
또한 모든 pixel들의 평균과 표준 편차를 이용하여 patch를 normalize하고, normalize를 통해 quality를 높일 수 있다.
ImageNet Experience
논문에서는 self-supervised pre-training에 ImageNet-1K dataset을 사용하였고, model의 representation을 평가하기 위해 supervised learning을 수행할 때 다음의 2가지 방법을 사용하였다.
- End-to-end fine-tuning
- Linear probing
Baseline으로는 ViT-Large[ViT_L/16]을 ablation study의 중추로 사용하였다. ViT-Large의 경우 ResNet-50보다 훨씬 더 크고 overfit 되는 경향이 있다.
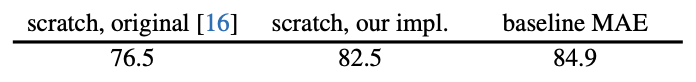
위의 결과는 ViT-L, strong regularization을 추가한 ViT-L, fine tuning을 사용한 MAE와의 supervised 결과에 대한 비교이다.
Main Properties
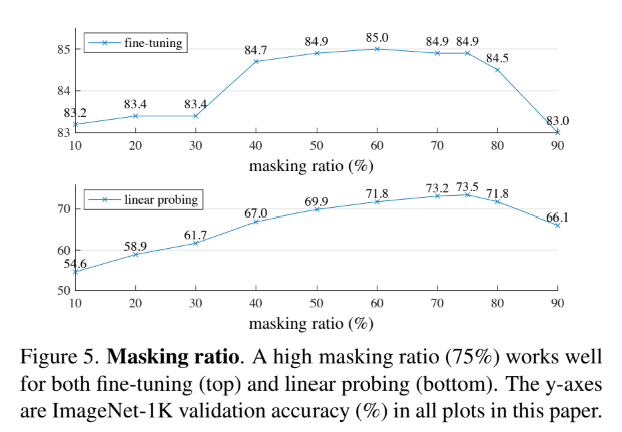
논문의 Masking ratio 그래프를 보면 알 수 있듯이 75%의 masking ratio에서 가장 높은 성능을 보이는 것을 알 수 있다.
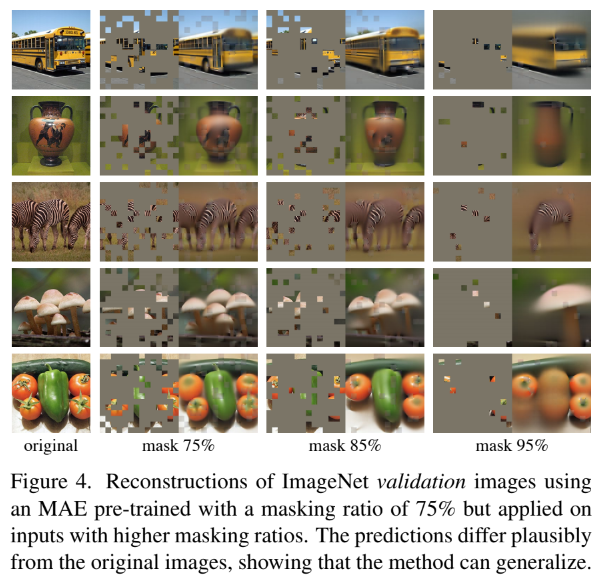
위의 그림을 보면 알겠지만, masking 비율을 높이게 되면 reconstruction의 결과가 blury 하지만 training time이 적게 걸리고 memory 소비도 줄어들어 MAE를 더 큰 model에도 쉽게 scaling 할 수 있게 된다.
심지어 BERT에서 15% masking한 것과 달리 MAE에서 무려 75%나 masking 했는데도 결과가 꽤나 정확한 것을 확인할 수 있다. 더하여 linear probing과 fine tuning과의 accuracy gap이 꽤나 유의미하고 fine-tuning의 경우 어떠한 masking ratio에서도 82.5%로 ViT scratch 성능보돠 높은 것을 확인할 수 있다.
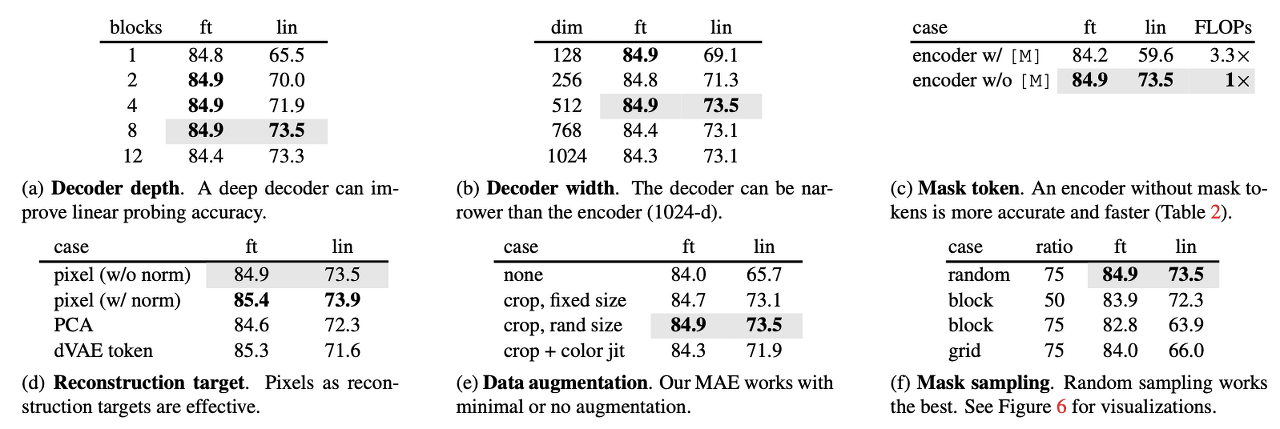
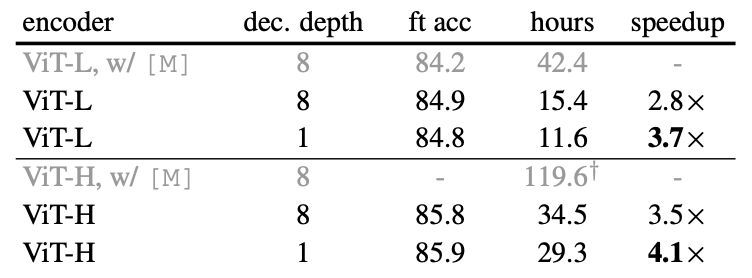
Decoder design
Decoder는 downstream에서 사용하지 않는다
Decoder depth에서 fine tuning은 block이 1개만 있어도 성능이 최고치를 달성하는 반면 linear probing의 경우 block의 개수에 따라 linear하게 성능이 올라가는 경향을 보인다. 저자들은 linear probing의 결과에 대해 encoder 뒤의 마지막 layer들에는 reconstruction을 위해 더 specialized 되지만 image recognition에서는 연관성이 적기 때문에 더 많은 개수의 layer가 필요하다고 주장한다.
이와 달리 fine-tuning 같은 경우는 encoder의 마지막 layer를 조정하여 image recognition에 적응하기 때문에 block이 1개 이상 존재하기만 해도 성능에 크게 영향을 주지 않아서 block 수를 줄여 lightweight한 decoder로 training이 가능하다.
Data Augmentation
MAE에서는 random horizontal flip, cropping 기법만을 사용하여 image augmentation을 하고 있다. 단순히 center-crop만 해도 잘 동작하는데 그 이유는 random masking이 augmentation 역할을 하기 때문에 각각의 iteration마다 다른 masking을 취하게 되어 data augmentation 없이 새로운 학습 데이터가 생성되게 된다. 이러한 masking 작업을 통해 pretext task를 더 어렵게 만들어 train regularization을 위해 적은 augmentation이 필요하다고 한다.

Discussion and Conclusion
Deep learning에서 가장 핵심이 되는 부분은 확장성과 간단함이다. NLP에서는 이미 GPT와 BERT 등 많은 model들이 생겨나고 있지만 Vision 분야는 아직 self-supervised learning보다는 supervised learning이 우세하다.
이 논문을 통해 저자들은 Transformer를 활용하여 Vision의 self-supervised learning 분야로의 확장 가능성을 제시하였다. 그러나 language와 image는 서로 다른 성격을 지니고 있는 signal이기 때문에 차이를 두고 접근을 해야 한다는 것을 강조하고 있다.
labeling 문제를 self-supervised learning을 통해 해결할 수 있는 가능성이 있기 때문에 이러한 연구가 계속되면 task 간의 장벽이 사라지고 더 좋은 성능을 지닌 model들이 많이 생겨나게 될 것이다.
